Tagomi Host
The Tagomi Host Contract is a central element of the Tagomi Protocol, acting as a hub connecting Super Tokens, Super Agreements, and Super Apps
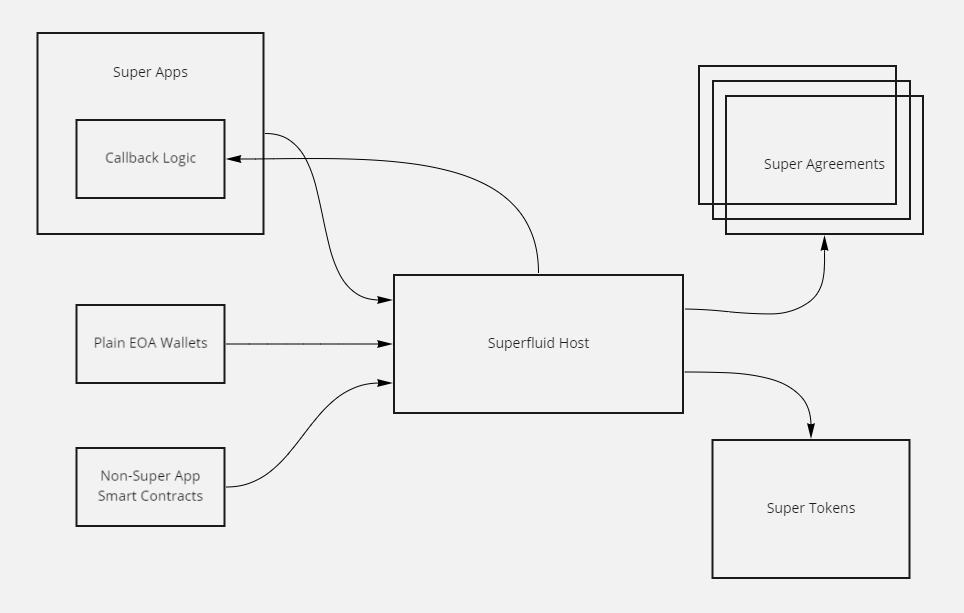
Tagomi Host Contract
Let's explore how the Host Contract interacts with different components of the Tagomi Protocol.
Super Agreements 🔗 Host Contract
Super Agreements, each with their unique contracts, interface with the Host Contract. Interaction with a Super Agreement is typically done by calling callAgreement() on the Host Contract, specifying the agreement and parameters.
Key Points
Upgradeability and Expansion: Super Agreements can be updated or new ones can be added and registered with the Host Contract.
info
NOTE: Direct interactions with Super Token contracts are not required for invoking Super Agreements. Instead, these agreements are accessed via the Host Contract, which then manages the Super Token balances involved.
Super Tokens 🔗 Host Contract
Super Tokens form the foundational layer of the Tagomi Protocol, where all Super Agreement data for an account is compiled.
Functionality
Aggregated Balance Calculation: The impact of each Super Agreement on an account's balance is cumulatively calculated to determine the Super Token balance.
Data Sourcing: Super Token contracts obtain necessary data through the Host Contract by iterating over the registered Super Agreements.
Super Apps 🔗 Host Contract
Registration of Super Apps with the Tagomi Host is essential to enable their callback functionalities.
Interaction Mechanics
Registration Requirement: Super Apps must be registered with the Host to function correctly.
Callback Activation: When a Super Agreement is engaged with a Super App, the Host Contract triggers the Super App's callbacks.
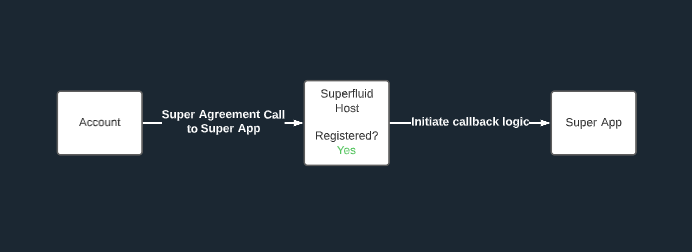
Super Apps and Host Contract
In summary, the Tagomi Host Contract is integral to the Tagomi Protocol, facilitating seamless interactions and integrations among Super Tokens, Super Agreements, and Super Apps.
Last updated
Was this helpful?